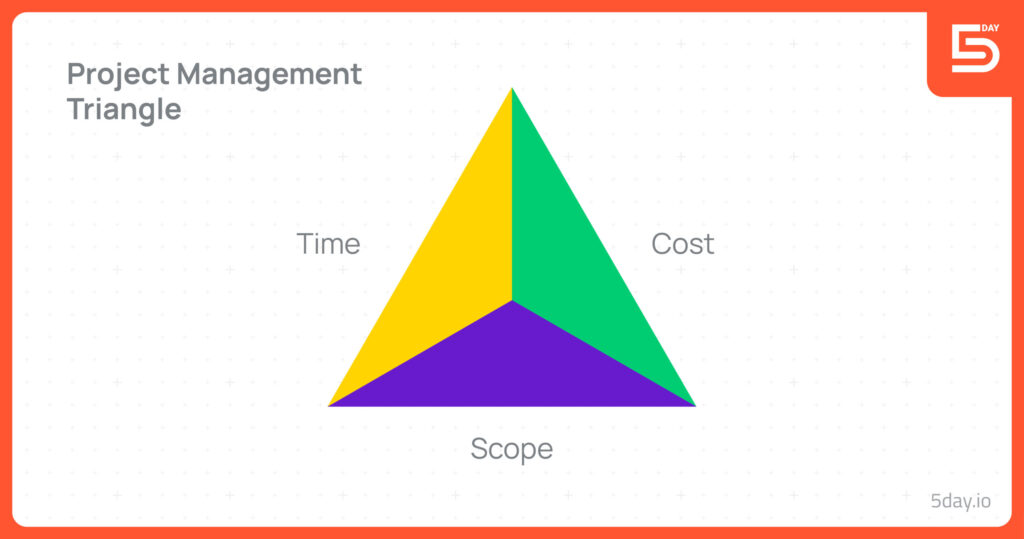
The project management triangle, also referred to as iron triangle, golden triangle or triple constraint, represents the inherent trade-offs between time, scope and cost in any project.
This simple yet powerful model shows that altering one constraint can impact the others. In this blog, we will explore what a project management triangle is, its benefits, and how you can manage project management constraints.
What is the project management triangle
Project management triangle is a framework for evaluating the information and demand in any project. Understanding the relationship of three domains – time, cost and scope is key to project success. In this model, the project scope is the function of cost and time, incurring trade-offs among these factors.
Scope = f (Cost, Time)
It is demonstrated as a simple triangle with each vertex as one of three different project constraints.
Scope constraints
Project scope refers to the task that must be done to deliver a product, service or result with defined features and functions. It includes the baseline of any project that outlines what is included and also, what is excluded. Key aspects of project scope are:
- Objectives: It is the overall goal or purpose of the project. These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time bound. It emphasizes the importance of business cases with scope statement.
- Deliverables: This defines the tangible products or services produced by the project. These are measurable outcomes that show project outcomes.
- Acceptance criteria: These are the conditions that should be met for deliverables to be considered satisfactory. These criteria should allow objective evaluation.
- Exclusions: This clearly states what is not included in the project scope. These exclusions help manage stakeholder’s expectations and prevent scope creep.
- Constraints: These are limitations or restrictions that can affect the project. These can include budget constraints, time constraints, or resource availability, etc.
You can’t increase the scope without increasing cost and time.
Cost constraints
Project cost determines the economic value of all resources utilized during the project. Cost refers to the resource needed for project execution. Here are different types of costs:
- Direct costs: These are directly linked to the project, such as labor, equipment, software license, etc.
- Indirect costs: These are not directly related to the cost object, such as administrative cost, rent, utilities, etc.
- Sunk costs: These are the kind of costs that are already incurred and can’t be recovered. These don’t influence future project decisions.
Costs can be further classified as:
- Fixed costs: These costs remain constant regardless of project progress, such as rent or software license.
- Variable costs: These costs fluctuate based on any project activity, such as labor or materials.
Budget overruns arise from an intricate combination of cost-related issues and broader project management challenges. Budget overruns are quite common in long term projects. These occur due to changes in scope, unexpected expenses, or poor initial estimates. The McKinsey report suggests that only 59 percent of projects are completed within budget.
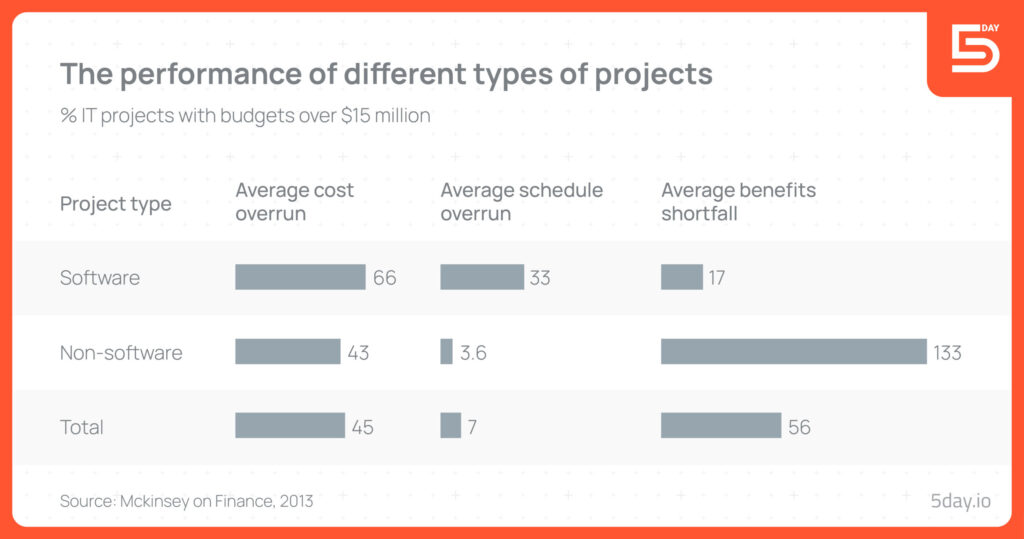
The performance of different types of projects
Time constraints
Time is the amount of time allocated or needed to complete the tasks within the project. Managing time often requires an adjustment of cost and scope. An estimation of all the factors like resource, time, or any potential bottleneck becomes important to calculate time.
Some of key components of time constraints are:
- Deadlines: These are specific dates by which deliverables or phases of the project must be completed. These are often by stakeholders, clients, or project requirements.
- Duration: These are time allotted for the project from initiation to closure. It influences resource allocation and task scheduling.
- Milestones: These are significant markers or checkpoints in the project. It ensures the project stays on track and allows for any adjustments if needed.
Even experienced project managers get it all wrong, as only 47 percent of IT projects are completed on time.
Good time management helps the team meet important deadlines and milestones.
How triple constraint works
The three constraints are interconnected and interdependent, that means change in one will impact others in any project.
If your project team is using either waterfall approach or agile methodology, it is important to understand what is fixed and what needs to be estimated. Agile development has a fixed schedule and resources, while scope is variable.
| Fixed | Variable |
Waterfall development | Scope | Resource, Time |
Agile development | Resource, Time | Scope |
Triangle facilitates visualizing the trade-offs inherent in project management. A project manager must carefully balance these constraints to achieve project success. Here’s how these constraints work:
Let’s define the constraints:
S: Scope (represented by the amount of work, features, or deliverables)
C: Cost (total allocated funds)
T: Time (project duration)
Fixed scope
- Increased cost: With more resources, tasks can be completed faster, shortening the timeline. This could be hiring more team members, investing in advanced tools or outsourcing some work.
- Reduced cost: Limited resources may extend the timeline to meet the fixed scope. It will include prioritizing tasks, or seeking alternatives, cost effective solutions.
In case of fixed scope (S = constant),
Increased cost (C) = Reduced time (T);
Reduced cost (C) = Increased time (T)
That means cost is inversely proportional to time, when scope is constant.
Fixed time
- Increased scope: Expanding the project’s deliverables while maintaining a fixed deadline will require a larger cost to manage the increased workload. This would require hiring additional resources.
- Reduced cost: Decreasing the budget while adhering to a fixed deadline might reduce the project scope. This could involve prioritizing essential features or scaling project deliverables.
In case of fixed time (T = constant),
Increased cost (C) = Increased scope (S);
Reduced cost (C) = Reduced scope (S)
That means cost is directly proportional to scope, when time is constant.
Fixed cost
- Increased scope: Increasing the project’s scope with a fixed cost will extend the timeline to manage the increasing workload for existing resources.
- Reduced timeline: Shortening the project timeline while maintaining a fixed cost might require reducing the scope. It involves focusing on core deliverables and simplified processes.
In case of fixed cost (C = constant),
Increased scope (S) = increased time (T);
Reduced scope (S) = reduced time (T)
That means scope is directly proportional to time, when cost is constant.
Importance of project management triangle
Project management triangle covers the trade-offs and interdependence of the three constraints with each other. Evaluation and optimization of these are vital for project success. Here’s why:
- Establish clear priorities: This illustrates the degree of change of one variable will impact other variables. For example, if you reduce the project timeline then it might incur additional cost and similarly reduce the project scope. Understanding the relationship of these variables allows project managers to make informed decisions and balance their priorities.
- Realistic expectations: It helps in setting the realistic expectations of the project with the stakeholders. Analysis of time, cost, scope and the trade-offs provide project managers with different scenarios and also limitations for any project. For example, if a stakeholder asks for an early delivery date, in that case the project manager can use the triangle to show how this can impact the cost or scope.
- Effective resource allocation: By understanding the constraints, project managers can allocate resources effectively to achieve the desired balance between time, cost, and scope. If scope is the top priority, resources might be focused on ensuring all features are delivered, even if it means a longer timeline or higher cost.
- Measuring project progress: It provides a framework for measuring project success. Analysis of the triple constraints helps project managers to identify any potential issues proactively and take corrective measures for that.
- Improved communication: By using this framework, project managers can ensure that all the team members, external members, contractors or stakeholders understand the project scope, cost and schedule. This helps in keeping all timelines, dependencies, and responsibilities on track for better collaboration and decision making.
While the traditional triangle focuses on time, cost, and scope, some variations include quality as a fourth constraint. This shows the importance of delivery of quality products or service while managing other constraints.
How to manage project triangle constraint
Managing the project triangle effectively requires careful planning, monitoring, and proactive adjustments. Here are several strategies to manage scope, time, and cost more effectively:
Define and document constraints
- Keep the documentation of all project deliverables, features, and functionalities in detail. Use work breakdown structure to break down projects into smaller, manageable tasks.
- Estimate costs for resources, materials, labor and other expenses. Consider contingency buffers for unforeseen issues.
- Develop a realistic project schedule, considering dependencies between tasks and resource availability.
Prioritize and balance
- Determine which constraint is most important for the project’s success. Is it delivering on time, staying within budget, or including scope. This outlines the importance of flexibility in at least one constraint.
- Understand the changes to one constraint will impact the others. If the scope increases, either the time or budget will need to be adjusted quickly.
Monitor and control
- Regularly track progress against the baselines for time, cost, and scope. Use project management tool to track actual performance versus planned performance.
- Analyze standard deviation of the data from the baseline and identify the root cause of the variance.
- Implement corrective actions to address variances and bring projects back on track. This might involve adjusting the scope, time, budget, or reallocating resources.
Collaborate
- Involve stakeholders early in decision making processes related to tradeoffs and changes to constraints.
- Provide transparency about the project’s status and challenges faced in managing the constraints.
Project management triangle example
Project managers frequently encounter challenging decisions when balancing the project management triangle. Consider a scenario, in a project where the stakeholders decided mid-project to add new features to the product.
This increase in scope necessitated adjustments in either time or budget to uphold the project’s quality. Originally, the project aimed to develop a basic application within three months on a limited budget. However, incorporating additional functionalities substantially broadened the scope. Faced with a critical decision, the project manager chose to prolong the deadline by approx. two months, allowing the team to integrate the new features without sacrificing quality. So, here are the two options presented to the project manager.
Consider software development project with initial parameters:
Scope: Basic app features (defined as 10 story points)
Time: 90 days (3 months)
Cost: $20,000 ($2000 per story point)
—————
*Story point is used to estimate required to complete a user story
Mid project, stakeholders requested additional features, increasing the scope. New change:
Scope increase: 5 additional story points (50% increase)
To maintain this, project manager has 2 options:
Option 1: Extend timeline
New scope: 10+5 story points
New timeline: 3 months + 1.5 months
Fixed cost: $20,000
Option 2: Increase budget
New scope: 15 story points
Fixed time: 3 months
New cost: $30,000
By quantifying the elements of the project management triangle, the decision-making process becomes more transparent, and data driven.
Conclusion
Understanding the interconnectedness of time, cost, and scope are essential for successful execution of projects. The project management triangle focuses the entire team on the key variables that determine the quality of the final deliverable. While the triangle features these three constraints, their interdependence presents a complex challenge. Using project management software can make the job easier for project managers.
5day.io takes out stress and guesswork out of time management. Unlike other project management software, it is easier to get started with. Try 5day.io and take back control over your project schedules.
FAQs
What is triple constraint in project management?
The triple constraint represents 3 main constraints in project management – scope, time, and cost. If one constraint changes, other constraints must also be adjusted to maintain quality.
What are the four elements of the project management triangle?
The project triangle consists of 3 constraints – time, scope, cost and when these are properly balanced, it produces the 4th element of project management triangle: quality
What are the top tools to manage project management triangle?
Top tools to manage project management triangle:
- 5day.io
- Clickup
- Wrike
- Monday.com
- Asana
- Teamwork





